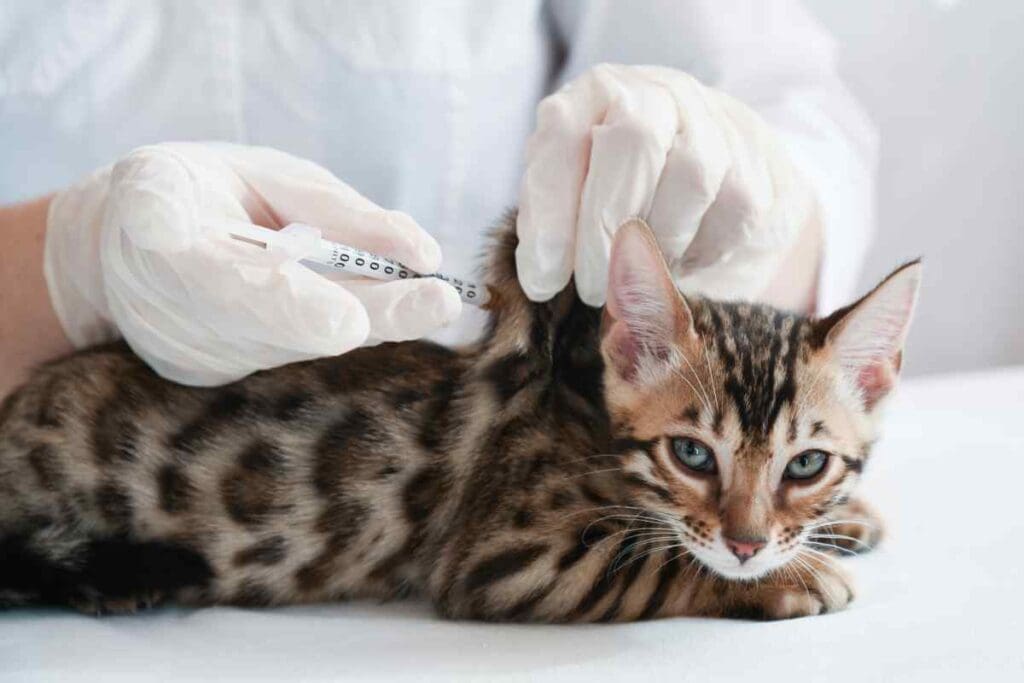
Protect Your Feline’s Health
Welcoming a new kitten or caring for an adult cat involves more than just providing food and shelter. One of the most critical aspects of responsible pet ownership is ensuring your feline companion receives proper vaccination. Cat vaccines play a crucial role in protecting their health by preventing the onset of serious and potentially life-threatening diseases. In this detailed guide, we will explore the importance of vaccines for cats, the essential vaccinations every cat should receive, and guidelines for maintaining a proper cat vaccination schedule.
Importance of Vaccines for Cats
Vaccines
protect cats against infectious diseases that can significantly impact their health and well-being. By stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against specific viruses and bacteria, vaccines prepare the body to recognize and fight off these pathogens if encountered in the future.
This proactive approach not only shields individual cats from illness but also contributes to the broader goal outlined in the cat vaccination guide of community immunity, thereby reducing the spread of contagious diseases among feline populations. The vaccine for cats can be among the preventive measures that play a crucial role in maintaining cat communities’ overall health and resilience, ensuring a safer and healthier environment for all feline companions.
Understanding Feline Vaccination
Essential Cat Vaccines
- Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis (FVR) and Feline Calicivirus (FCV): These respiratory viruses are the primary causes of upper respiratory infections in cats. Symptoms include sneezing, nasal discharge, and eye inflammation. Vaccination against FVR and FCV is essential for all cats, as these diseases are highly contagious and can spread rapidly in multi-cat households or environments with high cat density.
- Feline Panleukopenia Virus (FPV): Commonly known as feline distemper, FPV is a severe and often fatal viral disease that affects a cat’s gastrointestinal tract, immune system, and nervous system. Vaccination against FPV is crucial, particularly for kittens, as they are more susceptible to severe complications from the virus.
- Rabies: Rabies is a fatal viral infection that affects the central nervous system of mammals, including cats. It is transmissible to humans through bites or scratches from infected animals. Vaccination against rabies is not only vital for protecting your cat but is also mandated by law in many regions to prevent the spread of this zoonotic disease.
- Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV): FeLV is a retrovirus that weakens a cat’s immune system, making them susceptible to secondary infections, anemia, and certain types of cancer. Vaccination against FeLV is recommended for cats at risk of exposure, such as those who spend time outdoors or live in households with FeLV-positive cats.
Cat Vaccination Guide
Kitten Vaccination Schedule
- 6-8 weeks: Begin core vaccinations, including FVR, FCV, and FPV. Depending on risk assessment, vaccination against FeLV may also start.
- 10-12 weeks: Administer boosters for core vaccines to strengthen immunity acquired from initial vaccinations.
- 4-16 weeks: Administer the final boosters for core vaccines and administer the rabies vaccination if it has not been provided
- Annually: Schedule annual boosters for core vaccines and consider the necessity of FeLV vaccination based on your cat’s lifestyle and exposure risks.
Adult Cat Vaccination Schedule
- Annually: Continue administering annual vaccinations for core vaccines, including FVR, FCV, FPV, and rabies.
- FeLV Vaccination: Reevaluate the need for FeLV vaccination annually based on your cat’s health status and potential exposure to FeLV-positive cats.
Eline Vaccination: Ensuring Your Cat’s Health
Eline or feline vaccination encompasses a tailored approach to protecting cats against specific diseases by administering appropriate vaccines. This proactive measure not only safeguards individual cats but also contributes to feline communities’ overall health and resilience.
Guidelines for Feline Vaccination
- Consultation with a Veterinarian: Your veterinarian is a trusted partner in managing your cat’s health, including vaccination protocols tailored to their needs. Age, health status, lifestyle, and geographic location significantly determine the appropriate vaccination schedule.
- Core and Non-Core Vaccines: Core vaccines are recommended for all cats due to the widespread prevalence and severity of the diseases they prevent. Non-core vaccines may be recommended based on individual risk factors and environmental considerations.
- Vaccine Safety: Vaccines are generally safe for cats with rare adverse reactions. Mild reactions such as lethargy or mild fever may occur shortly after vaccination. Severe reactions are uncommon but should be reported promptly to your veterinarian for assessment and follow-up care.
- Lifetime Protection: Maintaining a consistent vaccination schedule ensures ongoing protection against infectious diseases throughout your cat’s life. Annual boosters for core vaccines help maintain strong immunity against potential threats in their environment.
Conclusion
Vaccines for cats are integral to their overall health and well-being, providing essential protection against preventable diseases. By adhering to a structured cat vaccination guide and collaborating closely with your veterinarian, you can ensure your beloved feline companion receives the necessary vaccines, including FVR, FCV, FPV, rabies, and FeLV. Eline vaccination offers peace of mind, knowing you are taking proactive steps to safeguard your cat’s health and longevity.
Vaccination protocols may vary based on individual circumstances and evolving medical recommendations. Regular consultations with your veterinarian allow for personalized vaccination plans that address your cat’s specific needs and ensure they lead a healthy, happy life free from preventable diseases.